 Everyone needs strong hips. Athletes need them to perform a wide variety of movements within a given sport. Aging adults need them to help reduce the risk of falls. When we think about the hip, most people think about the glutes and abductors. You can look in any gym and see a handful of people with a band around their knees performing a plethora of movements working the glutes and abductors. However, the most neglected muscle is the one on the inside of the thigh: the adductor.
Everyone needs strong hips. Athletes need them to perform a wide variety of movements within a given sport. Aging adults need them to help reduce the risk of falls. When we think about the hip, most people think about the glutes and abductors. You can look in any gym and see a handful of people with a band around their knees performing a plethora of movements working the glutes and abductors. However, the most neglected muscle is the one on the inside of the thigh: the adductor.
Anatomy and Function of the Adductor
The adductor muscle is situated in both the medial and posterior compartments of the upper leg. It attaches to the hip bone and to the linea aspera of the femur. The primary role of the adductor is to adduct and internally rotate the thigh at the hip joint. It also plays an important role in hip extension and stabilizing the pelvis along with the glutes and hamstrings.
Why You Should Be Training the Adductors
The adductors are a secondary muscle group that assists the larger muscle groups during compound exercises such as squats and deadlifts. However, there are important benefits to focusing accessory movements on the adductors. As I mentioned, the adductor plays a role in hip extension and stabilization of the pelvis. Hip extension is one of, if not the most powerful movements of the body. It is how we jump, stand, walk, run, and sprint. If we neglect the adductor muscles, we are missing out on added stabilization of the pelvis during all these movements.
Groin strains are the most common among athletes who are sprinting, cutting, and changing directions. Throughout these movements, the adductors take on a large load of eccentric forces. This means that just like the hamstrings during a heel strike, these muscles are force absorbers. A muscle is more likely to tear or strain if it is not strong enough to absorb an increasing amount of force. Strengthening the adductors can reduce the likelihood of a groin strain.
The adductors not only stabilize the pelvis, but they also control pelvic rotation. This is highly important for sports such as baseball, softball, golf, hockey, or tennis. All of these sports rely highly on the rotational power of your hips for swinging and throwing. Weak adductors will not help you hit farther or throw harder.
Movements for the Adductors
- Adductor Machine: Not all gyms or facilities have one of these machines. However, if you do have access to one, it’s the simplest way to directly train the adductors.
- Adductor Foam Roller Hold: Although you do not get the same overloading stimulus as the adductor machine, the foam roll hold could be a substitute for the machine. For this variation, all you need is a foam roller, or an object similar in width and it needs to be solid. In a seated or lying position, bend your knees to 90* and place the foam roller between your knees and squeeze. This is an isometric movement that you can make harder by holding for a longer duration.
- Banded Adduction: For this you will need a super band and a place to anchor the band close to the ground. To perform this movement, you will be in a standing position with your side to the band. Wrap the band around the inner foot and step out until you feel tension on the band. From your starting point, let the band pull your foot away. Stand tall and bring your foot back to the center.
- Lateral Lunge: This is a great movement for any skill level because it can be progressed and regressed. To perform a body-weight lateral lunge, start with both legs together. Step one foot out and begin to bend that knee and start to sit your hips back. Push off that leg and bring both feet together. To progress this movement, simply add weight.
- Copenhagen Plank: For this movement you will need a bench or a box. You will start in a side plank position with your top foot on the bench and your bottom leg either straight or bent. From this position, you will pick your hip up and hold.
- Medicine Ball Scoop Pass: For the rotational action of the adductors, we will perform a rotational throw. With a medicine ball in both hands, shift your weight to the outside foot. From this position, push off the outside foot and rotate the hips, and then the shoulders, and throw the ball at the wall.
This blog was written by Evan James, NIFS Exercise Physiologist EP-C, Health Fitness Instructor, and Personal Trainer. To learn more about the NIFS bloggers, click here.


 The
The  Chances are if you are like me, you have been told your whole life, “Make sure you’re stretching, it’s important!” But to many, the first thought that pops into their head when they think about stretching is, “Why?” And that is a very understandable response because stretching can involve a lot of discomfort (in the beginning) and to some, it might even cause a bit of pain. But there certainly is a method to the madness, and a reason why stretching is a vital component of your fitness program and, ultimately, your lifestyle.
Chances are if you are like me, you have been told your whole life, “Make sure you’re stretching, it’s important!” But to many, the first thought that pops into their head when they think about stretching is, “Why?” And that is a very understandable response because stretching can involve a lot of discomfort (in the beginning) and to some, it might even cause a bit of pain. But there certainly is a method to the madness, and a reason why stretching is a vital component of your fitness program and, ultimately, your lifestyle.  Thousands of sports nutrition supplements are touted to improve strength, endurance, and a variety of other athletic factors. But do they work and are they necessary? Below are some of the most common supplements advertised for athletes, as well as what they do, how well they work, and how much is safe to supplement. It’s important to note that you should always consult your physician or a registered dietitian specializing in sports medicine before starting any new supplement.
Thousands of sports nutrition supplements are touted to improve strength, endurance, and a variety of other athletic factors. But do they work and are they necessary? Below are some of the most common supplements advertised for athletes, as well as what they do, how well they work, and how much is safe to supplement. It’s important to note that you should always consult your physician or a registered dietitian specializing in sports medicine before starting any new supplement. More and more in today’s society, people have one resource that seems like it is only getting stretched out thinner and thinner: time. Too many of us seem to be cramming more and more things into our lives, whether that be work-related events, personal interests, or family events. With this ever-growing list of things we have taking time out of our day, many have to choose between stuff they need to get done and things they want to get done. One thing we all know we should do but sometimes choose to skip because of time constraints is exercising.
More and more in today’s society, people have one resource that seems like it is only getting stretched out thinner and thinner: time. Too many of us seem to be cramming more and more things into our lives, whether that be work-related events, personal interests, or family events. With this ever-growing list of things we have taking time out of our day, many have to choose between stuff they need to get done and things they want to get done. One thing we all know we should do but sometimes choose to skip because of time constraints is exercising. The
The 
 How I Did It
How I Did It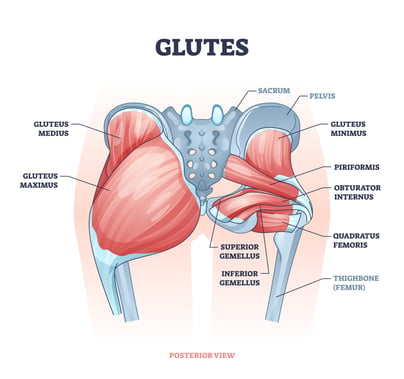 The Gluteal Muscles
The Gluteal Muscles.jpg?width=532&height=342&name=GettyImages-1083005864(1).jpg) Muscle Mass Gains
Muscle Mass Gains