 In the most basic definition, plyometrics refers to jump training. Known to be a key component of many sports, such as basketball, soccer, gymnastics, and football, plyometric training can enhance athleticism, strengthen the most powerful muscles in your body, and much more.
In the most basic definition, plyometrics refers to jump training. Known to be a key component of many sports, such as basketball, soccer, gymnastics, and football, plyometric training can enhance athleticism, strengthen the most powerful muscles in your body, and much more.
Here are some of the benefits of plyometric exercises, and how to safely add plyometrics to your workout routine.
The Benefits of Plyometrics
For you to propel your body off the ground and land safely, many things have to happen in your muscles, tendons, ligaments, and joints. Studies show that plyometrics can help you build muscle as effectively as conventional weightlifting, and if you combine the two, it can help you reach your goals faster than focusing on either one alone. Also, the impact your body absorbs from landing has benefits for your bones: they become stronger.
If you are an athlete, plyometrics can improve your agility and explosiveness when it comes to fast-response moves, such as sprinting, quick direction changes on the field or court, and jumping (such as going for a header in soccer).
How to Get Started with Plyometrics
If plyometrics is new to your workout, as with anything you should start small. This is especially important for plyometric exercises. Correct form is crucial, as you need to both lift your body off the ground and control the landing. This dual action makes plyometric exercises more difficult and complex than most exercises. If you have a movement deficiency, it will be magnified when the speed and power of a jump are applied to it.
When learning a new plyometric move, you should first perform the move without the jump to perfect the form, strength, and stability that is required to do it correctly. Once you have all of that, you can then add the jumping movement. Another way to start small is to choose lower-impact plyometric exercises, such as jumping jacks, jumps in place, and line hops (side to side, forward, and back).
Do not ignore the upper body: plyometric pushups and medicine ball throws are great for building explosive power above the waist. Always be aware of your form. When you become tired, your form tends to suffer, and the risk of injury increases.
Is there anyone who shouldn’t do plyometric exercises? The short answer is no, as long as your doctor has not identified a reason why you should not (such as deteriorating joints or bad knees). If you are significantly overweight, gradually adding plyometrics is the key—and stay away from high-impact moves altogether. Remember that doing too much too soon—or doing advanced exercises before you are ready for them—can stress your joints, increasing your risk of injury.
This blog was written by David Behrmann, NIFS Health Fitness Instructor.To learn more about the NIFS bloggers, click here.


 Running with others is one of the most effective strategies for creating a running habit and continuing it. The social benefits of running are among the biggest reasons why runners start and stick with running. Whether you’re running with one friend or a running group, here are some ways you can benefit from group running.
Running with others is one of the most effective strategies for creating a running habit and continuing it. The social benefits of running are among the biggest reasons why runners start and stick with running. Whether you’re running with one friend or a running group, here are some ways you can benefit from group running. How many times have you or someone you know needed help because they were unable to open the pickle jar? Now, how many times have you heard someone get mad because the pickle jar was too easy to open. I’m guessing you haven’t. Nobody has ever complained about being too strong—a statement I like to tell people when they ask why they should start strength training. There are many benefits of strength training. As we age we lose the physical ability to carry out certain activities. Tasks that were once easy are now difficult to do alone or not at all. These are our activities of daily living.
How many times have you or someone you know needed help because they were unable to open the pickle jar? Now, how many times have you heard someone get mad because the pickle jar was too easy to open. I’m guessing you haven’t. Nobody has ever complained about being too strong—a statement I like to tell people when they ask why they should start strength training. There are many benefits of strength training. As we age we lose the physical ability to carry out certain activities. Tasks that were once easy are now difficult to do alone or not at all. These are our activities of daily living. 
 For many athletes and recreational athletes, the arrival of winter and cold weather usually signifies the end of their athletic season. Once the bulk of your outdoor sport competition has concluded or slowed down, reflections of the past year take place. You may have run a personal record in your first 5K, mini, or full-marathon; had your best record in your tennis league; or had the lowest scoring average over a spring and summer for golf. Whatever your sport is or whatever you worked on that previous off-season, the wheels start churning in your mind about how you might be able to continue that improvement for the next season.
For many athletes and recreational athletes, the arrival of winter and cold weather usually signifies the end of their athletic season. Once the bulk of your outdoor sport competition has concluded or slowed down, reflections of the past year take place. You may have run a personal record in your first 5K, mini, or full-marathon; had your best record in your tennis league; or had the lowest scoring average over a spring and summer for golf. Whatever your sport is or whatever you worked on that previous off-season, the wheels start churning in your mind about how you might be able to continue that improvement for the next season.  When watching elite athletes during competition, there are many athletic traits and features that we novices or amateurs marvel at. We think to ourselves, “If I did something like that, I wouldn’t walk for a week!” Seeing an NFL running back or wide receiver make a cut at full speed, a baseball player hitting a 400-foot home run, or a powerlifter deadlifting the weight of a Volkswagen Beetle are feats that just leave you in awe.
When watching elite athletes during competition, there are many athletic traits and features that we novices or amateurs marvel at. We think to ourselves, “If I did something like that, I wouldn’t walk for a week!” Seeing an NFL running back or wide receiver make a cut at full speed, a baseball player hitting a 400-foot home run, or a powerlifter deadlifting the weight of a Volkswagen Beetle are feats that just leave you in awe.  In a world where people want results in an instant and take drastic measures to achieve those results as fast as possible, developing strength, power and athleticism in a long-term aspect is often overlooked. For any fitness-related result or outcome, improvements take time. Fat loss, overall strength and/or power in any particular lift, speed, and agility are all seeds that needed to be watered for a while before noticeable and permanent changes are evident.
In a world where people want results in an instant and take drastic measures to achieve those results as fast as possible, developing strength, power and athleticism in a long-term aspect is often overlooked. For any fitness-related result or outcome, improvements take time. Fat loss, overall strength and/or power in any particular lift, speed, and agility are all seeds that needed to be watered for a while before noticeable and permanent changes are evident. As an athlete there is no substitute for the ability to produce power and be explosive during your sport. From competitive weightlifters and NFL-caliber football players to distance runners, producing (and absorbing) high impacts is crucial for succeeding in your sport as well as staying healthy throughout your competition season. Are you incorporating any of these exercises into your current program?
As an athlete there is no substitute for the ability to produce power and be explosive during your sport. From competitive weightlifters and NFL-caliber football players to distance runners, producing (and absorbing) high impacts is crucial for succeeding in your sport as well as staying healthy throughout your competition season. Are you incorporating any of these exercises into your current program? Agility drills basically represent an obstacle. Athletes who can respond faster to starts, stops, and change of direction earlier than the obstacle will have a practical advantage on the playing field. This blog highlights three of my favorite agility drills that can be built into your team’s conditioning routines. The benefits of these runs, jumps, and cuts include increases in reactionary speed, coordination, footwork, and body awareness. Athletes need to be able to change direction rapidly under control without decreases in speed.
Agility drills basically represent an obstacle. Athletes who can respond faster to starts, stops, and change of direction earlier than the obstacle will have a practical advantage on the playing field. This blog highlights three of my favorite agility drills that can be built into your team’s conditioning routines. The benefits of these runs, jumps, and cuts include increases in reactionary speed, coordination, footwork, and body awareness. Athletes need to be able to change direction rapidly under control without decreases in speed.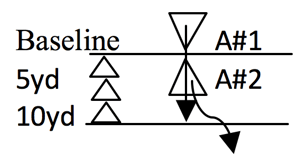 Drill 1: Offense/Defense—Partner Reaction Acceleration Tag
Drill 1: Offense/Defense—Partner Reaction Acceleration Tag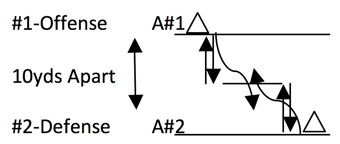 Drill 2: Cat & Mouse—5-5 Shuttle Reaction Tag
Drill 2: Cat & Mouse—5-5 Shuttle Reaction Tag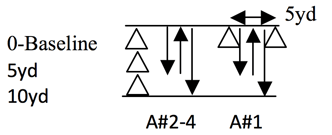 Drill 3: Shuttle Runs—Reaction 5-5-10 Shuttle
Drill 3: Shuttle Runs—Reaction 5-5-10 Shuttle Once the competitive season begins, scheduling time to get in to lift is a lot more difficult due to the practices, games, and travel that are happening. To me, in-season lifting is sometimes undervalued in the competitive/athletic world because of the fact that the primary focus is to win games or matches, not lift weights. However, I believe that this is one of the most important (if not the most important) times during the year because of what lifting can do for the athlete throughout the competitive season and into the off-season.
Once the competitive season begins, scheduling time to get in to lift is a lot more difficult due to the practices, games, and travel that are happening. To me, in-season lifting is sometimes undervalued in the competitive/athletic world because of the fact that the primary focus is to win games or matches, not lift weights. However, I believe that this is one of the most important (if not the most important) times during the year because of what lifting can do for the athlete throughout the competitive season and into the off-season.  In NFL and college football, each week, a star player is hit with a sidelining injury. Possibly lost for multiple weeks, months, or at worst, the whole season. Injuries that are usually the result of bad luck or not being as physically prepared as they could have been. Hopefully your team, **knock on wood**, does not or will not have to deal with this at any point during their season. My team, my beloved
In NFL and college football, each week, a star player is hit with a sidelining injury. Possibly lost for multiple weeks, months, or at worst, the whole season. Injuries that are usually the result of bad luck or not being as physically prepared as they could have been. Hopefully your team, **knock on wood**, does not or will not have to deal with this at any point during their season. My team, my beloved  As you can see, progression of strength (and power with other lifts) has to be maintained year round. This goes for all athletes throughout their seasons. If they want to continue to improve, they must prevent the loss. It is as important of a cycle of training as any. Without a properly structured in-season maintenance phase, you will be starting from the same place every time you start a new offseason training program.
As you can see, progression of strength (and power with other lifts) has to be maintained year round. This goes for all athletes throughout their seasons. If they want to continue to improve, they must prevent the loss. It is as important of a cycle of training as any. Without a properly structured in-season maintenance phase, you will be starting from the same place every time you start a new offseason training program.