As we continue down the road of improving our basic movement patterns (which is always under construction, by the way), we take a look at the squat pattern and its variations a bit further. Many fitness pros, including myself, argue that we spend more time on one leg than we do on two. Think about it: walking, running, traveling up stairs—for varying amounts of time, you can find yourself on one leg a lot.
What Makes a Split Squat a Split Squat?
So if you are on one leg a bunch, it only makes sense that you build that position to be strong and stable, and in many different planes of motion. Let’s take a look at what makes a split squat a split squat, which is very different from the lunge but often is called by the same name (kind of a pet peeve of mine).
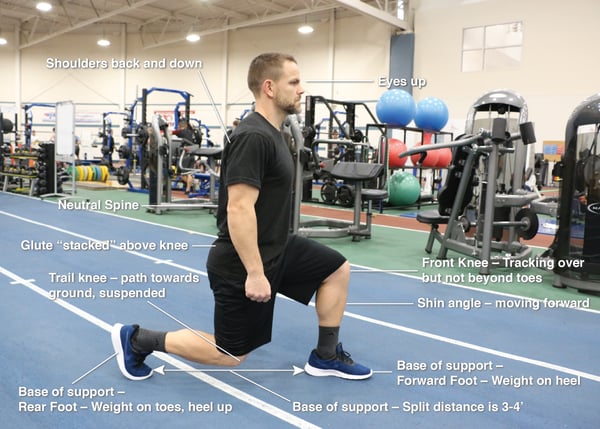
- Base of support—Forward Foot – Weight on heel
- Base of support—Rear Foot – Weight on toes, heel up
- Base of support—Split distance is 3-4’
- Shin angle—moving forward
- Front Knee – Tracking over but not beyond toes
- Trail knee – path towards ground, suspended
- Glute “stacked” above knee
- Neutral Spine
- Shoulders back and down
- Eyes up
Many of the aspects of the regular squat are found in the split. You are simply in a single-leg-supported position.
Options to Get More Out of the Split Squat
Now that you have the foundation, here are a few options you can use to get more out of this movement pattern.
- TRX Split Squat
- 2KB Split Squat—Farmer position
- 1KB RFEE Split Squat—Down position
- 2KB Split Squat-Racked position
Exercise Variations in the Frontal and Transverse Planes
Human beings need to travel in 3D. It’s important to all of us, from the athlete to the accountant. Often we train in one plane of motion, typically the sagittal plane (in the regular squat, for example, or the overhead press). But in the real world we move in more ways than straight ahead. Here are some variations that will get you in the frontal (side-to-side) and the transverse (rotational) planes.
- 3D Body Weight
- Offset KB Spit Squat
- SaB Lateral Split Squat
- SaB + KB Rot. Split Squat
The split squat is a super-important movement pattern that I feel we need to train more. As single-leg beings, mastering this pattern in multiple planes will transfer big time to the real world and allow us to move better, more often, with fewer injuries.
Like what you've just read? Click here to subscribe to our blog!
This blog was written by Tony Maloney, ACSM Certified Exercise Physiologist and Fitness Center Manager. To find out more about the NIFS bloggers, click here.