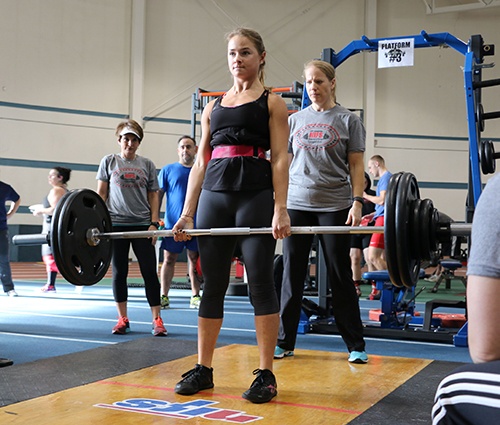 The deadlift is a creature all its own. There is no other exercise like it, and there are so many reasons behind that. It can be one of the most beneficial total-body exercises, yet at the same time, one of the most detrimental if performed incorrectly. Numerous factors go into this very important lift, but there are a few tricks to keep in mind to help you set up and perform well consistently while avoiding injury.
The deadlift is a creature all its own. There is no other exercise like it, and there are so many reasons behind that. It can be one of the most beneficial total-body exercises, yet at the same time, one of the most detrimental if performed incorrectly. Numerous factors go into this very important lift, but there are a few tricks to keep in mind to help you set up and perform well consistently while avoiding injury.
1. A straight line is the fastest path to your destination.
The deadlift starts at the floor and ends at a fully upright stance. There are no two ways about that. Isn’t the quickest way from point A to point B a straight line? Absolutely. This means that the path of the bar during the lift should be as straight as possible. If you’re saying “I have no idea whether my bar path is straight,” take a quick video of your deadlift from the side. A great smartphone app for this is Iron Path. It lets you track your bar path, and it has definitely helped me out.
2. Learn how to breathe and use a belt.
People ask whether they should wear a belt. There is no one-size-fits-all answer here. It completely depends on why you are wearing a belt in the first place. Contrary to popular belief, wearing a lifting belt will not save your back from bad deadlifting. Bad deadlifting (for example, rounding of the back) will place a lot of torque on your entire spine, and this is why most deadlifting injuries occur. A belt is not your safety net. The proper use for a belt is to, along with proper breathing, help create intra-abdominal pressure to brace the midsection for a heavy lift.
First, learn to breathe correctly. If the lift is heavy (80% or greater of your 1-rep max), you will want to take in a big breath before every rep and brace your abdominals and obliques to maintain spinal alignment. Once you can deadlift with proper breathing, a belt becomes helpful during your heavy lifts.
3. Determine your best stance.
I can’t tell you what your best stance is. You will have to find out on your own. The two traditional stances used are conventional and sumo stance. With conventional, your feet will be somewhere around shoulder width apart. With sumo stance, your feet will be much wider (typically 6 to 8 inches outside shoulder width). Certain body types tend to work better for each style. For example, someone who is considered to be tall and lanky might have a good chance of being a better conventional-style deadlifter. Certain limb lengths create different leverages that give advantages and disadvantages with each style of deadlifting. Long story short: try both.
***
Done correctly, the deadlift is one of the best overall exercises out there. It is a closed-chain, multi-joint movement that involves lower- as well as upper-body strength, stability, and mobility. Warning: the deadlift is not easy, and you may have to lighten up the weight to get the correct technique. Give these tips a try and make sure you ask a NIFS Health Fitness Specialist for more help with technique and how to better yourself as an athlete.
This blog was written by Aaron Combs, NSCA CSCS and Health Fitness Instructor. To find out more about the NIFS bloggers, click here.


 Building muscle is perhaps the most common goal (second to fat loss) of an exercise program. Many people eventually hit a plateau with exercise routines and muscle-gaining processes and find it increasingly difficult to continue putting on new muscle. Once the body becomes too familiar with certain exercises or a certain style of training, your results will be hindered.
Building muscle is perhaps the most common goal (second to fat loss) of an exercise program. Many people eventually hit a plateau with exercise routines and muscle-gaining processes and find it increasingly difficult to continue putting on new muscle. Once the body becomes too familiar with certain exercises or a certain style of training, your results will be hindered. 

 Okay, so maybe you’re not a morning person, and would much rather remain cozy in your queen-sized bed for several hours after waking up before finally finding the energy and motivation to make your way to the gym during the middle of the day. Maybe you’re the type of person who likes to take care of your priorities first during the day, and then only if left with enough time sneak in a late-afternoon or nighttime workout before ending your day.
Okay, so maybe you’re not a morning person, and would much rather remain cozy in your queen-sized bed for several hours after waking up before finally finding the energy and motivation to make your way to the gym during the middle of the day. Maybe you’re the type of person who likes to take care of your priorities first during the day, and then only if left with enough time sneak in a late-afternoon or nighttime workout before ending your day.
 This is the final installment in my series on training for people 40 and over. Previously I’ve discussed
This is the final installment in my series on training for people 40 and over. Previously I’ve discussed  In earlier installments, I’ve talked about
In earlier installments, I’ve talked about 
 This is a pretty common question that comes to mind for me. I work out 6 days a week, but still that mild ascent up four flights of stairs to the copy room seems to get me every time.
This is a pretty common question that comes to mind for me. I work out 6 days a week, but still that mild ascent up four flights of stairs to the copy room seems to get me every time.  You have finally achieved your goal of adding some lean muscle mass, so what now? Where do you go next? The next step I would take would be to train your body to use those newly developed muscles to their fullest potential. This increase in strength building can come from numerous sources, some of which you may have already experienced.
You have finally achieved your goal of adding some lean muscle mass, so what now? Where do you go next? The next step I would take would be to train your body to use those newly developed muscles to their fullest potential. This increase in strength building can come from numerous sources, some of which you may have already experienced.  We use fitness for many reasons, sometimes for stress, weight loss, or performance. Relatively speaking, the role of the Fitness Specialist has not been around as long as most professions, but it has had some very drastic and conflicting concepts and theory clashes, contradictions and discrepancies. These concepts and theories are ever changing and evolving to meet the criteria and need of scientific research, human nature and what actually works. Of note, one such theory that needs to be put to bed is the idea that we can “spot reduce” by simply focusing on a specific body part.
We use fitness for many reasons, sometimes for stress, weight loss, or performance. Relatively speaking, the role of the Fitness Specialist has not been around as long as most professions, but it has had some very drastic and conflicting concepts and theory clashes, contradictions and discrepancies. These concepts and theories are ever changing and evolving to meet the criteria and need of scientific research, human nature and what actually works. Of note, one such theory that needs to be put to bed is the idea that we can “spot reduce” by simply focusing on a specific body part.