The fourth and final movement pattern of this blog series is the hip hinge. If you have not read it already, head to the original blog post, Optimal Movement Patterns for Building Muscle, which gives an overview of the four-movement patterns that everyone should be training. In this post, I go over the hip hinge movement pattern.
 The Hip Hinge Pattern
The Hip Hinge Pattern
The hip hinge movement pattern is a compound movement that works the muscles of the low back, glutes, and hamstrings. These muscles are also known as the “go” muscles. The hinge pattern is an essential movement for your activities of daily living such as bending over, getting up from the floor, and walking. It is also essential to train this pattern to strengthen the muscles of the lower back around the spine. These muscles, as well as the glutes and hamstrings, can become very weak if you work a desk job or are sedentary for most of your day.
Training the hip hinge movement pattern to a full range of motion can also improve the flexibility in your hips and hamstrings. Learning how to hinge properly should be an essential aspect of your training from the beginning. Within your training plan, you can break this movement down into bilateral and unilateral patterns, just like the squat pattern. Bilateral means both legs working at the same time, and unilateral means one leg at a time. Utilizing both bilateral and unilateral will ensure you are not creating any imbalances between your legs. You can also isolate the muscles utilized in the hip hinge pattern, the hamstrings, and the glutes.
Hip Hinge Variations
Bilateral
- Barbell Deadlift
- Kettlebell Deadlift
- Hex Bar Deadlift
- Barbell Romanian Deadlift
- Dumbbell Romanian Deadlift
- Barbell Goodmornings
- Seated Goodmornings
- Hip Thrusts
- Glute Bridges
- Kettlebell Swings
Unilateral
- Kickstand Deadlift
- Single-leg Romanian Deadlift
Hamstring Isolation Movements
- Prone Leg Curl
- Seated Leg Curl
- Banded Leg Curl
Glute Isolation Movements
- Glute Kick Backs
- Hip Abduction (band or machine)
- Glute Ham Raises
- Glute Focus Back Extensions
Get Help with Your Training Program
For more information on how to properly progress and structure a training program, visit our staff at the track desk to schedule a private session. We are more than happy to help at any time, and as part of your membership here at NIFS, you receive complimentary workout programs. Our Health Fitness professionals tailor all programs to your fitness goals.
This blog was written by Evan James, NIFS Exercise Physiologist EP-C, Health Fitness Instructor, and Personal Trainer. To learn more about the NIFS bloggers, click here.


 The first thought that comes into most people’s heads when they hear the word weightlifting is, more times than not, “bulky.” The perception is that heavy weightlifting will cause an undesired large gain of muscle mass. This is true; weightlifting will cause you to put on muscle mass, but it will take a lot more than just lifting weights to be “bulky.” Please do not let your goals steer you away from certain exercises.
The first thought that comes into most people’s heads when they hear the word weightlifting is, more times than not, “bulky.” The perception is that heavy weightlifting will cause an undesired large gain of muscle mass. This is true; weightlifting will cause you to put on muscle mass, but it will take a lot more than just lifting weights to be “bulky.” Please do not let your goals steer you away from certain exercises.
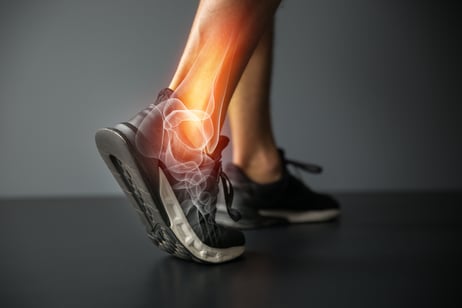 Whether you are a seasoned workout veteran or the new face in the gym, there’s no denying that lower-leg pain can be a huge deterrent for exercise (and day-to-day life, for that matter). Some pains are dictated by the range of motion in the ankle. Due to several factors including previous injuries and wear and tear, physiological problems from the various shoes people wear, and the types of exercises people punish their bodies with, we see individuals every day who have a hard time performing some of the more basic exercises such as squats and deadlifting.
Whether you are a seasoned workout veteran or the new face in the gym, there’s no denying that lower-leg pain can be a huge deterrent for exercise (and day-to-day life, for that matter). Some pains are dictated by the range of motion in the ankle. Due to several factors including previous injuries and wear and tear, physiological problems from the various shoes people wear, and the types of exercises people punish their bodies with, we see individuals every day who have a hard time performing some of the more basic exercises such as squats and deadlifting. When you hear the word stretch, you might think immediately about flexibility (or perhaps your lack thereof). Flexibility was always the term used for enhancing limited movement, until the word mobility arrived and took the fitness industry by storm.
When you hear the word stretch, you might think immediately about flexibility (or perhaps your lack thereof). Flexibility was always the term used for enhancing limited movement, until the word mobility arrived and took the fitness industry by storm. What Is Functional Training?
What Is Functional Training?
 Many people shy away from lifting weights because they think it will make them “big and bulky.” To bring a little more clarity to that notion, please see
Many people shy away from lifting weights because they think it will make them “big and bulky.” To bring a little more clarity to that notion, please see  The
The  If you have spent any amount of time in the gym lately, I am sure you have seen a lot of people using exercise bands for part of their workout. When looking at a flimsy, thin exercise band, many would think, “Okay, what type of workout will that even give me?” Studies have shown that workouts using exercise bands will increase muscle strength and size while helping decrease fat, similar to using free weights.
If you have spent any amount of time in the gym lately, I am sure you have seen a lot of people using exercise bands for part of their workout. When looking at a flimsy, thin exercise band, many would think, “Okay, what type of workout will that even give me?” Studies have shown that workouts using exercise bands will increase muscle strength and size while helping decrease fat, similar to using free weights. 

 move pretty well at one test, it will eventually find a restriction or asymmetry/imbalance at some point if you have any. Our job is to identify any weaknesses, limitations, imbalances, or asymmetries so that we can immediately prescribe you a corrective strategy to reduce your chance for injury and increase fitness results.
move pretty well at one test, it will eventually find a restriction or asymmetry/imbalance at some point if you have any. Our job is to identify any weaknesses, limitations, imbalances, or asymmetries so that we can immediately prescribe you a corrective strategy to reduce your chance for injury and increase fitness results.