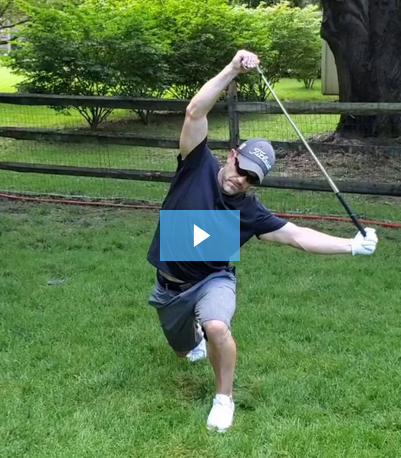
In part 4 of this series on squats, I focus on body weight again, setting up lower-body conditioning routines you can do at home, outside in the park, or in the hotel when you’re on the road. These are some of my favorite go-to workouts when I’m on the road or don’t have time to get in a quick leg workout. As I have reiterated throughout this blog series (part 1, part 2, and part 3), regardless of your fitness goals, you can and should add some form or fashion of squats to your fitness routines.
A Quick Workout: AMRAP Challenge
This video is a 6-minute lower-body AMRAP challenge. Your goal is to follow the routine and complete the series for as many rounds as possible (AMRAP) in the 6 minutes. Keep in mind, if you’re a beginner, start with less time (start with 4 minutes) or fewer reps of the combination. I love doing this quick workout when time is limited and I need to get in a quick lower-body workout.
Follow order:
- Reverse Lunge
- BW Squat
- Reverse Lunge
- BW Squat
- Box Jump
- BW Squat (on Box)
- Step-down
- BW Squat
A Tougher Lower-body Workout
When I’m on the road but do have time to get a tough lower-body workout completed, I like completing the following six series combined for a workout. Start with the first video and work your way through all six challenges. This has a variety of work to be completed, from EMOMs (Every Minute on the Minute) to Ladders (x1–10 Reps). Again, keep in mind, if you’re a beginner, start with less time, fewer reps, or a combination of the six challenges. As you advance, add more time or complete more than one challenge together if time allows. Also, if time is short, just like the 6-minute lower body challenge, complete one of the challenges instead of all six.
CHALLENGE 1: 10 minutes EMOM (Every Minute on the Minute) x15 Bodyweight Squats
CHALLENGE 2: 3 rounds x15 R/L—Rear Foot Elevated Split Squats
CHALLENGE 3: 5 rounds x5 Reps—Squat Jumps w/Floor Taps
CHALLENGE 4: x10min EMOM (Every Minute on the Minute) x10 Single-leg Bridges (R/L)
CHALLENGE 5: Burpee Ladder x1–10 x1 Rep x2 Reps x3 Reps... x8 Reps x9 Reps x10 Reps—Finished
CHALLENGE 6: Alternating Split Squat Lunge Jumps—Ladder x1–10 x1 Rep x2 Reps x3 Reps... x8 Reps x9 Reps x10 Reps—Finished
Get “King of the Gym” Results Outside the Gym
Whether you’re taking a break from heavy back squats or just need variety, or possibly you’re on the road traveling, you have ways to focus on your lower-body strength without a barbell and rack. Throughout the four posts in this series, Instead of adding more weight to your back squats, you’re changing up the exercises to make it more difficult and challenging. Your squats can progress in a similar way if you’re not barbell back squatting: You can start by doing air squats with both legs, then progress to split squats, and eventually one-legged pistol squats, which are a lot more challenging. On the road, focus on body weight again and set-up lower-body conditioning routines.
As I have reiterated in each of the preceding posts, regardless of your fitness goals, some form or fashion of squats can and should be added to your fitness routines. The end result for your lower body is similar to what you can get from working out with “king of the gym” back squats.
This blog was written by Michael Blume, MS, SCCC; Athletic Performance Coach. To learn more about the NIFS bloggers, click here.


 We all know that core stability and strength is an important factor in exercise, athletics, and even daily living. Being able to properly brace and stiffen the core is an important skill in preventing lower-back injuries when attempting certain movement patterns that occur every day. The abdominal crunch, which people often think of as a core exercise, is actually not a movement we see in our day-to-day lives. Try and think of a time you have had to mimic the abdominal crunch under a heavy load: it simply does not occur.
We all know that core stability and strength is an important factor in exercise, athletics, and even daily living. Being able to properly brace and stiffen the core is an important skill in preventing lower-back injuries when attempting certain movement patterns that occur every day. The abdominal crunch, which people often think of as a core exercise, is actually not a movement we see in our day-to-day lives. Try and think of a time you have had to mimic the abdominal crunch under a heavy load: it simply does not occur.  When watching elite athletes during competition, there are many athletic traits and features that we novices or amateurs marvel at. We think to ourselves, “If I did something like that, I wouldn’t walk for a week!” Seeing an NFL running back or wide receiver make a cut at full speed, a baseball player hitting a 400-foot home run, or a powerlifter deadlifting the weight of a Volkswagen Beetle are feats that just leave you in awe.
When watching elite athletes during competition, there are many athletic traits and features that we novices or amateurs marvel at. We think to ourselves, “If I did something like that, I wouldn’t walk for a week!” Seeing an NFL running back or wide receiver make a cut at full speed, a baseball player hitting a 400-foot home run, or a powerlifter deadlifting the weight of a Volkswagen Beetle are feats that just leave you in awe.  In my experience over the years working with folks from all walks of life to help improve their strength, mobility, performance, and overall fitness I have found that so many suffer from immobility in two major joints: the ankle and the shoulder, which is the focus of this piece. Lifestyle, occupation, inactivity, and overtraining are all culprits robbing so many of healthy range of motion in the shoulder and shoulder girdle.
In my experience over the years working with folks from all walks of life to help improve their strength, mobility, performance, and overall fitness I have found that so many suffer from immobility in two major joints: the ankle and the shoulder, which is the focus of this piece. Lifestyle, occupation, inactivity, and overtraining are all culprits robbing so many of healthy range of motion in the shoulder and shoulder girdle.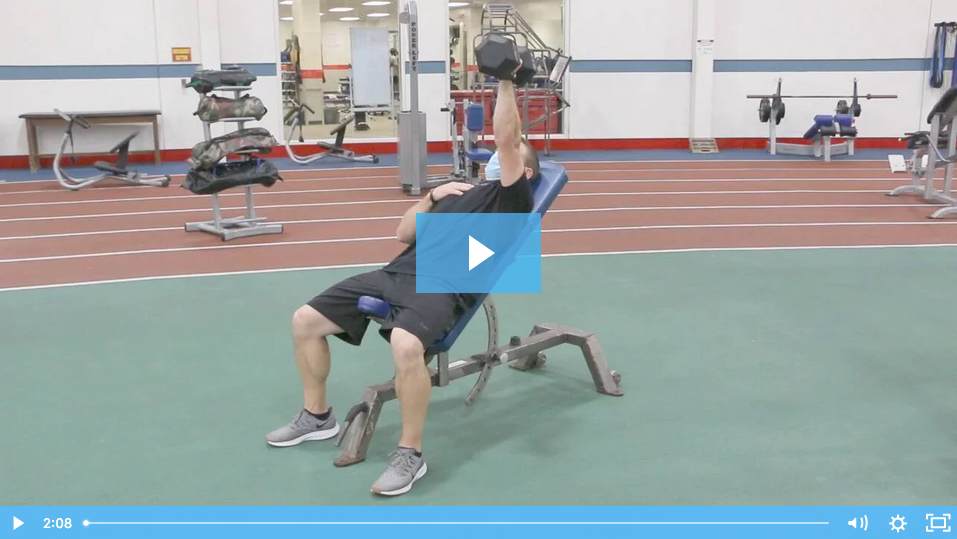 
 Looking back on the history of my work in the blog world, I have found that
Looking back on the history of my work in the blog world, I have found that 