
Whether you are 18 or 80, man or woman, looking to lose weight or simply maintain, step class just might be the perfect addition to your fitness program. Have you ever considered taking a step class? Perhaps you have found yourself thinking, "I'm not coordinated enough," or “that's too intense for me (or not intense enough"). Well, give me two minutes to change your mind.
Does It Burn Calories?
The bottom line is, stepping up and down off of a raised platform burns calories. In fact, it burns a lot of calories. According to Self magazine, stepping up and down off of a raised platform burns more calories than doing jumping jacks, split lunges, power squats, or speed skating for the same length of time. A great exercise for weight loss? YES! Great way to maintain weight? YOU BET!
Am I Coordinated Enough?
Maybe you’re thinking that you lack the required coordination. But the reality of it is, if you can march in place, you can do step. The basic step is just that: basic. Up, up, down, down. Of course that move would get boring pretty quickly, so we add music, rhythm, and variations on that basic move. While it helps to have a little rhythm (can you clap your hands to the beat of a song?), anyone can step. It might take a few classes to really get the hang of it, but it is quite doable, and FUN! Don't be intimidated!
There is a first time for everything. At some point, every single person in the class, including the instructor, attended their very first step class. I’m not gonna lie, you probably won't pick up every single thing in the first class you take, but let's face it: what would be the fun of mastering it in the first hour? Half the fun is seeing yourself improve, seeing your cardiovascular fitness level improve, and becoming more efficient overall (more work with less effort). Step will get you there!
Is It Too Intense?
You might be thinking that step would be too hard or too intense for you. While step is designed to be a challenging cardio workout, the intensity level can be adjusted in a number of ways to meet the needs of each participant.
- The height of the platform is not uniform; with use of individual risers at each end, the platform can be set as low as just a few inches off the floor (or as high as 8–12 inches).
- Another easy adjustment, which your instructor will show you, is to limit your range of movement with each step. As you become more comfortable with the format, you will be able to add intensity by increasing range of motion with the steps, and by adding arm movements to further increase your heart rate. Because of this, the challenge never ends. There is no plateau.
Is It Not Intense Enough?
On the flip side, maybe you are thinking step is not intense enough. Perhaps you’re thinking that only girls take step, or that you are too fit to benefit from it. Regardless of your fitness level, step can be a very challenging cardiovascular workout. It is a well-known fact that the US military utilizes step aerobics to improve our troops' agility, coordination, and endurance. If it's tough enough for our soldiers, then it's tough enough for me! In addition to step, I also teach Insanity, total-body conditioning, and kickboxing classes. Step meets or exceeds these other formats in intensity level and calories burned per hour.
Step is the perfect group fitness format because it accommodates all fitness levels. (And if you haven't tried group fitness, well that's a whole other conversation.) But in short, try it! The camaraderie and accountability among the participants, the music, and the FUN factor will have you hooked!
So, are you ready to take your fitness regimen to the next STEP? See you in class soon, soon, soon!
Yours in fitness,
Rachel
This blog was written by Rachel Pfeiffer, ACE and AFAA Certified Group Fitness Instructor, and proud NIFS Step instructor since 1999.

 How do you define fitness? Whatever your answer is, it will shape the way you work out, influence the goals you set, and impact your long-term health. Although everyone might have different perceptions of what “fitness” means, the American College of Sports Medicine has defined what
How do you define fitness? Whatever your answer is, it will shape the way you work out, influence the goals you set, and impact your long-term health. Although everyone might have different perceptions of what “fitness” means, the American College of Sports Medicine has defined what 
 Cycling is becoming one of the most popular trends in group fitness. Not only is it a great class to take for the cardio benefits and calorie burn, cycling is a great resistance-based workout that can also increase strength. Many cycling classes are tracked in two ways, by
Cycling is becoming one of the most popular trends in group fitness. Not only is it a great class to take for the cardio benefits and calorie burn, cycling is a great resistance-based workout that can also increase strength. Many cycling classes are tracked in two ways, by  Whether you are 18 or 80, man or woman, looking to lose weight or simply maintain,
Whether you are 18 or 80, man or woman, looking to lose weight or simply maintain, 
 With millions of people around the world suffering from back pain, is there any hope for relief outside of traditional methods? Low back pain can be excruciating and immobilizing, but there is still hope. When dealing with any pain or injury, exercising might be the last thing that crosses your mind, especially if it’s chronic low back pain (CLBP). However, that’s exactly what is recommended and what can help.
With millions of people around the world suffering from back pain, is there any hope for relief outside of traditional methods? Low back pain can be excruciating and immobilizing, but there is still hope. When dealing with any pain or injury, exercising might be the last thing that crosses your mind, especially if it’s chronic low back pain (CLBP). However, that’s exactly what is recommended and what can help.


 Getting healthy and losing weight go hand in hand. If your goal is to get healthy and lose weight, I need you to RELAX! No, really! Relaxing is good for you, and managing stress effectively doesn’t only help with weight loss; it makes us healthier overall. So sit back, relax, and read on for more tips.
Getting healthy and losing weight go hand in hand. If your goal is to get healthy and lose weight, I need you to RELAX! No, really! Relaxing is good for you, and managing stress effectively doesn’t only help with weight loss; it makes us healthier overall. So sit back, relax, and read on for more tips.
 Have you tried TRX class at NIFS? For starters, you may be asking yourself, “What is a trx?” TRX is a body-weight suspension training system designed to give you a total-body workout, while playing to your skill set and allowing for nearly limitless body-weight–oriented exercise. TRX can provide a fitness beginner with an opportunity to learn movement patterns properly as well as challenge the most seasoned veterans in the gym with more advanced progressions.
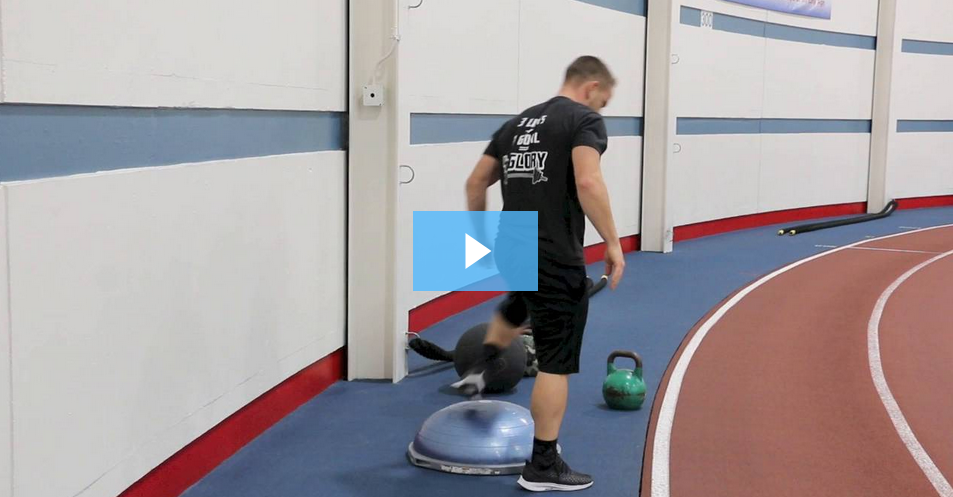
Have you tried TRX class at NIFS? For starters, you may be asking yourself, “What is a trx?” TRX is a body-weight suspension training system designed to give you a total-body workout, while playing to your skill set and allowing for nearly limitless body-weight–oriented exercise. TRX can provide a fitness beginner with an opportunity to learn movement patterns properly as well as challenge the most seasoned veterans in the gym with more advanced progressions. TRX Row: With two handles set to the short length (one tick mark), start with arms long and body in a plank position, being mindful that you do not let your hips sag. While under control, pull yourself up to your hands. Lower back down under control. PRO TIP: You can pull with your hands parallel to the floor to engage the lats more, whereas pulling with your hands horizontal to the floor works the rear deltoids and trapezius. (See video
TRX Row: With two handles set to the short length (one tick mark), start with arms long and body in a plank position, being mindful that you do not let your hips sag. While under control, pull yourself up to your hands. Lower back down under control. PRO TIP: You can pull with your hands parallel to the floor to engage the lats more, whereas pulling with your hands horizontal to the floor works the rear deltoids and trapezius. (See video  Group Fitness
Group Fitness Specialty Classes are Included in NIFS Group Fitness Schedule
Specialty Classes are Included in NIFS Group Fitness Schedule 
 You either love them or you hate them… group workouts! In a world where technology is seemingly taking over the human connection and interaction, working out with a group can offer the opportunity to meet real friends instead of virtual ones online.
You either love them or you hate them… group workouts! In a world where technology is seemingly taking over the human connection and interaction, working out with a group can offer the opportunity to meet real friends instead of virtual ones online.